Soluble PD-1 are the native equivalent of synthetic monoclonal anti-PD-L1, several of which are currently undergoing cancer trials as checkpoint inhibitors: Roche’s Atezolizumab, AZ’s Durvalumab, Merck’s Avelumab.
Immune cells in diseases like RA overproduce sPD-1, which binds PD-L1 on other immune cells, thereby blocking the latter’s ligation of PD-1 on T-cells to wind down the inflammation. sPD-1 can therefore also serve as a marker of autoimmune disease activity.
Use of anti-PD-L1 in cancer immunotherapy follows the same logic: it keeps alive the activated T-cells to fight the cancer. Measuring the levels of natural anti-PD-L1 antibodies may also serve to gauge tumour burden or the susceptibility of the tumour to PD-1/PD-L1 directed immunotherapy.
Prospects for Targeting PD-1 and PD-L1 in Various Tumor Types

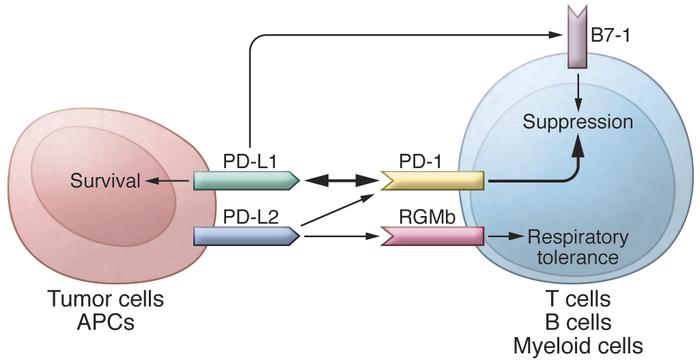
PD-L1 inhibition may theoretically be safer than inhibiting CTLA4 or PD-1, with less broad-based T-cell activation causing autoimmune phenomena. This is because it does not block ligation of PD-1 by PD-L2, which is expressed only by (self-)antigen-presenting macrophages and dendritic cells to downregulate potential autoimmunity.