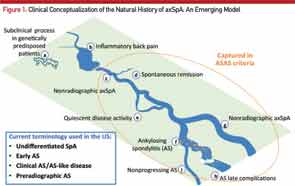
New Guideline: NSAIDs Effective in Treating Ankylosing Spondylitis & Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis

The question behind this question is really whether NSAIDs have a disease-modifying function (in preventing AS structural progression towards ankylosis), or is it merely a symptom-relieving anti-inflammatory, in which case it can be stopped once pain is gone or inflammation is controlled by “stronger” medicines like the anti-TNFs.
This paper provides a straightforward answer to the previous question (which is, “maybe, but we can’t be sure”), and a commonsensical approach to the management of AS that is both cost-effective yet personalised (“full-dose NSAID is first-line”). Read it.
Is NSAID to AS like MTX is to RA? The data is not robust enough to recommend that AS patients needing an anti-TNF for adequate disease control should stay on an NSAID as well to forestall structural progression; but the trend is suggestive.