Alzheimer Disease
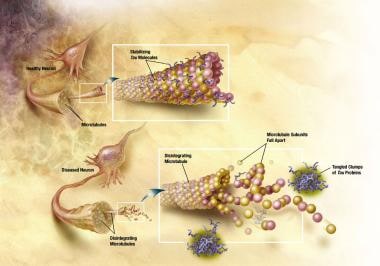
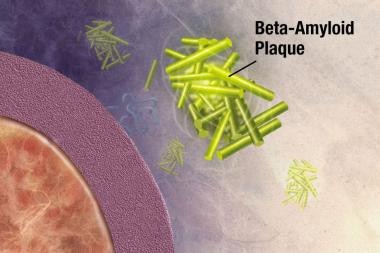
Alzheimer disease (AD) is an acquired disorder of cognitive and behavioral impairment that markedly interferes with social and occupational functioning. It is an incurable disease with a long and…
emedicine.medscape.com
Human amyloid-beta acts as natural antibiotic in the brain: Alzheimer’s-associated amyloid plaques may trap microbes

sciencedaily.com
Mapping The Brain’s Microbiome: Can Studying Germs In The Brain Lead To A Cure For Alzheimer’s?
forbes.com
Alzheimer’s Disease and Amyloid: Time to Move On?

2016 ended with the failure of yet another…
Medscape.com
The first-in-human clinical trial targeting Alzheimer’s tau protein
For the first time, targeting the other feature of Alzheimer’s disease, tau, has given fruitful results. In an unprecedented study, active vaccination in humans has resulted in a favorable immune response in 29 out of the 30 patients with only minor side effects.
sciencedaily.com
Leucomethylthioninium salts (LMTX) by TauRx Therapeutics
TauRx Therapeutics Ltd is a life sciences/pharmaceutical company incorporated in Singapore with primary research facilities and operations in Aberdeen, Scotland.[1][2]
en.wikipedia.org
Anti-TNF Drugs May Protect Against Alzheimer’s
ATLANTA — Treating rheumatoid arthritis patients with anti-tumor necrosis factor (TNF) drugs appears to lessen their likelihood of developing Alzheimer’s disease, according to a study reported here.
medpagetoday.com
Rapid cognitive improvement in Alzheimer’s disease following perispinal etanercept administration
jneuroinflammation.biomedcentral.com
New compound discovered in fight against inflammatory disease
A ten year study by University of Manchester scientists for a new chemical compound that is able to block a key component in inflammatory illness has ended…
manchester.ac.uk
Boron-Based Inhibitors of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
secure.jbs.elsevierhealth.com
Given the spectacular and consistent failure of Alzheimer’s treatments targeting Tau and Amyloid beta, and emerging evidence that such proteins serve important structural and defence functions (and are therefore epiphenomenal rather than etiological), perhaps the way forward is to target the final common pathway which is the immune response to possible yet-unidentified dysbiotic trigger(s): the NLRP3 inflammasome.

